40 kinetic energy label
› physics › energy-potential-kineticPotential and Kinetic Energy - Math is Fun Kinetic energy (KE) is energy of motion. A moving car has a lot of kinetic energy. From PE to KE. These skydivers have potential energy due to being high up. After they jump this potential energy gets converted into kinetic energy (and heat) as they speed up. Pendulum. For a good example of PE and KE have a play with a pendulum. Gravitational ... Kinetic and Potential Energy - Wyzant Lessons Kinetic energy can be quantified as one half of the mass times the velocity squared (KE = 1/2*m*v²). In SI units, the mass should be in kilograms (kg), and the ...
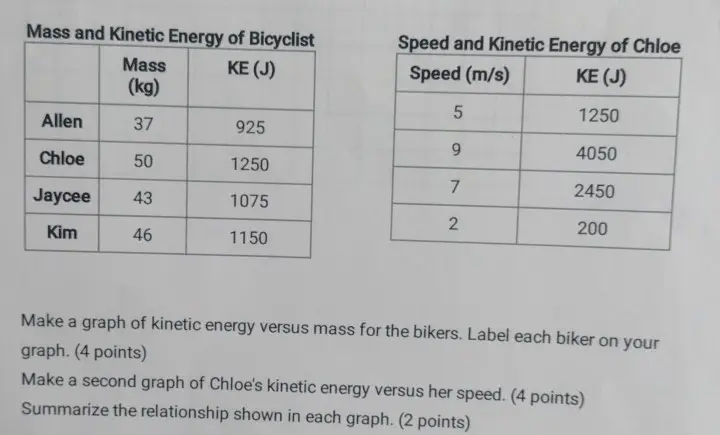
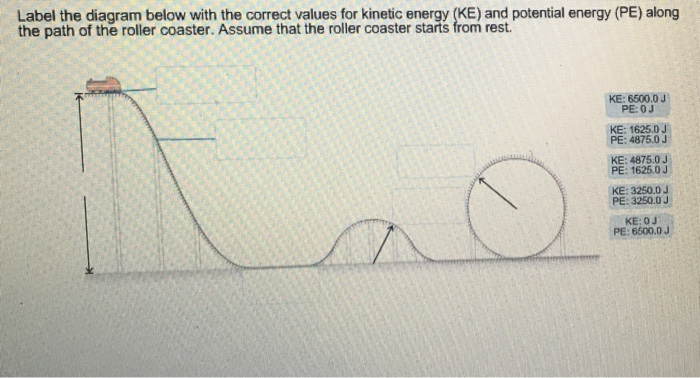
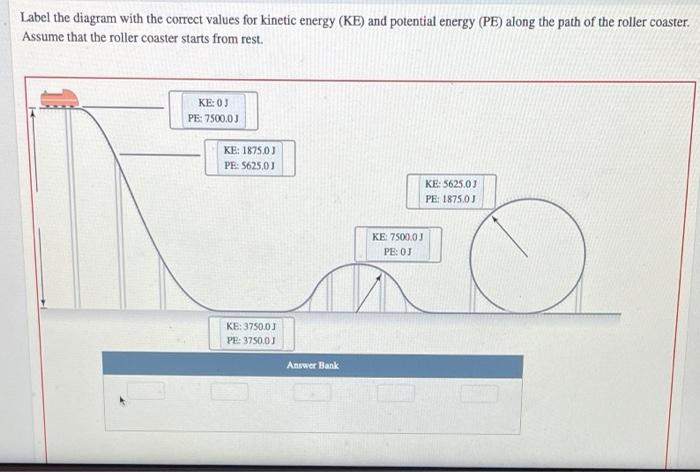
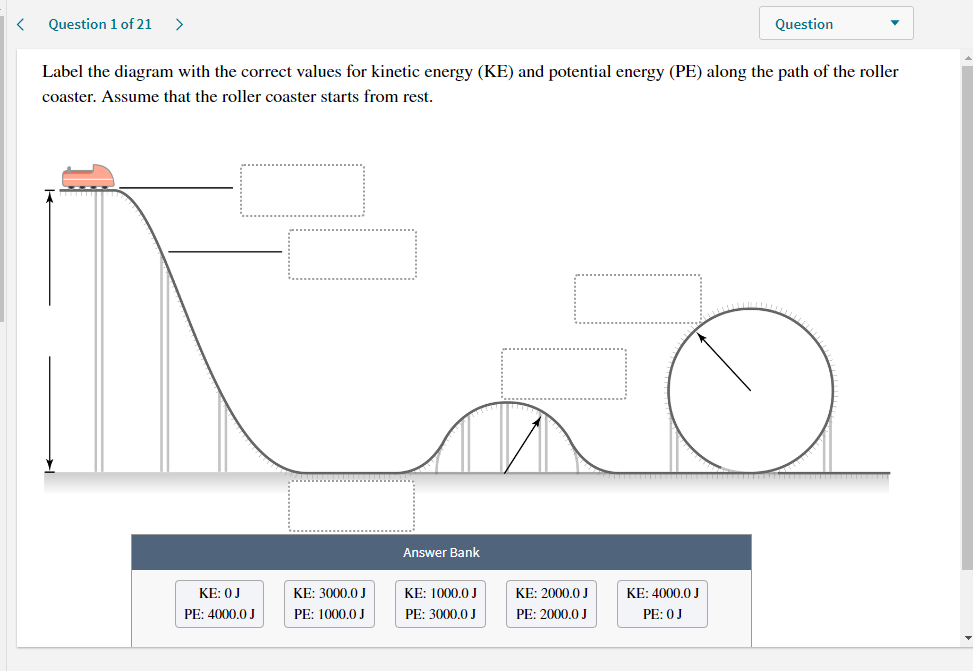
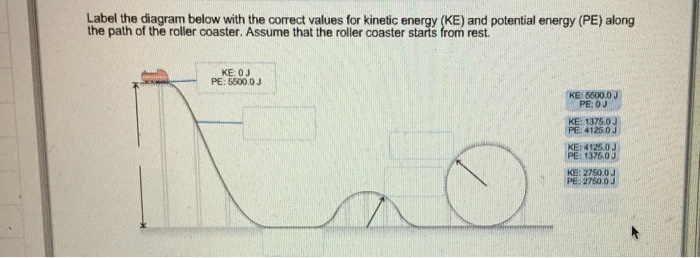
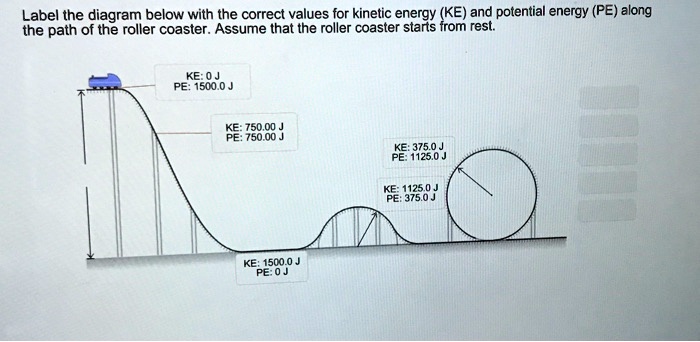
Solved Label the diagram with the correct values for kinetic - Chegg Label the diagram with the correct values for kinetic energy (KE) and potential energy (PE) along the path of the roller coaster. Assume that the roller coaster starts from rest. KE: OJ PE: 5500,0J KE: 1375.0J PE: 4125.03 KE: 5500,0J PE: OJ KE: 4125.0J PE: 1375.00 Answer Bank KE: 2750.0) PE: 2750.0 Incorrect This problem has been solved!
Kinetic energy label
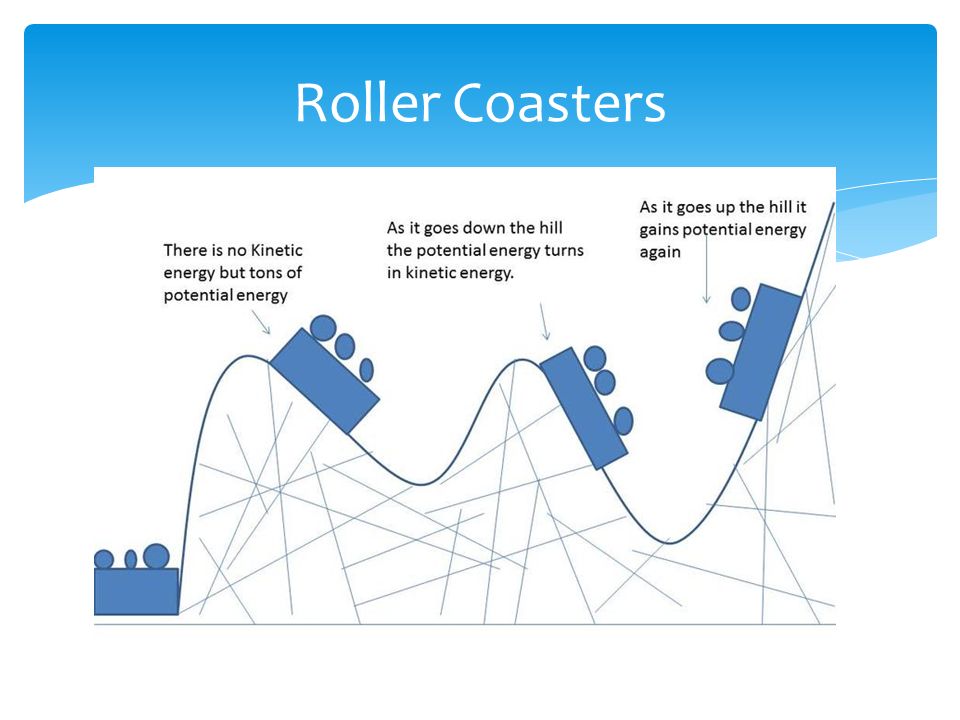
Kinetic energy - Wikipedia The kinetic energy is equal to 1/2 the product of the mass and the square of the speed. In formula form: where is the mass and is the speed (magnitude of the velocity) of the body. In SI units, mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules . phys.libretexts.org › Bookshelves › College_Physics7.2: Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem Feb 20, 2022 · Kinetic energy is a form of energy associated with the motion of a particle, single body, or system of objects moving together. We are aware that it takes energy to get an object, like a car or the package in Figure, up to speed, but it may be a bit surprising that kinetic energy is proportional to speed squared. Paper Roller Coasters: Kinetic and Potential Energy Roller coasters are an excellent way to teach your students about conservation of energy. Gravitational * potential energy is the amount of energy an object has due to its mass and its height off the ground. Kinetic energy is the amount of energy an object has due to its mass and its speed. When a roller coaster car reaches the top of its very ...
Kinetic energy label. What is Kinetic and Potential Energy? [Stored Energy ... - YouTube Aug 23, 2022 ... We define energy as the ability to do work or the ability to change. Change in energy can take place in various forms. Label the diagram with the correct values for kinetic energy (KE) and ... Kinetic energy (K.E): it is an energy possessed by an object or body due to its motion. Furthermore, the mechanical energy of a physical object or body is the sum of the potential energy (P.E) and kinetic energy (K.E) possessed by an object. Mathematically, mechanical energy is given by the formula; Potential vs kinetic energy label - Teaching resources - Wordwall Potential vs. Kinetic Energy (Maze Chase) - Kinetic vs. Potential Energy - Potential vs. Kinetic Energy - Potential vs Kinetic Energy Sort. Drag each label to the correct location on the chart. The answers would be: POTENTIAL ENERGY --- Energy of compressed spring --- Energy of coal KINETIC ENERGY --- Energy of a guitar string when plucked. --- Energy from a flashlight when turned on. If you'd like to know why: Energy can be divided into two broad categories, which are: Potential and Kinetic energy.
chem.libretexts.org › Bookshelves › General_Chemistry9.14: Kinetic Theory of Gases- The Total Molecular Kinetic Energy Jul 20, 2022 · The kinetic energy of an individual molecule is ½ m ( u2) ave, and so the average kinetic energy ( Ek) ave of a collection of molecules, all of the same mass m is ( E k) ave = ( 1 2 m u 2) ave = 1 2 m ( u 2) ave The total kinetic energy Ek is just the number of molecules times this average: E k = N × ( E k) ave = N × 1 2 m ( u 2) ave › physics › kinetic-energyKinetic Energy Calculator Feb 13, 2023 · The kinetic energy formula defines the relationship between the mass of an object and its velocity. The kinetic energy equation is as follows: KE = 0.5 × m × v², where: m – Mass; and v – Velocity. With the kinetic energy formula, you can estimate how much energy is needed to move an object. How to Calculate Kinetic Energy: 9 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow The formula for calculating kinetic energy (KE) is KE = 0.5 x mv2. Here m stands for mass, the measure of how much matter is in an object, and v stands for velocity of the object, or the rate at which the object changes its position. [8] Your answer should always be stated in joules (J), which is the standard unit of measurement for kinetic energy. What Is Kinetic Energy? | Live Science The kinetic energy of an object is the energy it has because of its motion. In Newtonian (classical) mechanics, which describes macroscopic objects moving at a small fraction of the speed of light ...
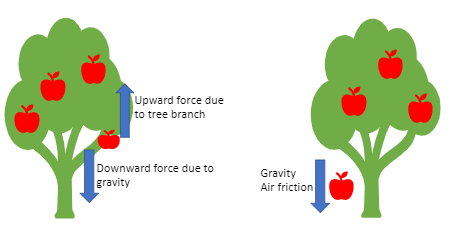
Thermodynamics: Kinetic and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is usually measured in units of Joules (J); one Joule is equal to 1 kg m2 / s2. Calculate the kinetic energy in Joules possessed by each of the ... What is kinetic energy? (article) | Khan Academy Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its motion. If we want to accelerate an object, then we must apply a force. Applying a force requires us to do work. After work has been done, energy has been transferred to the object, and the object will be moving with a new constant speed. Label Services Kinetic Label Services specializes in high volume, durable label products. We work with compliance intensive specifications and custom applications. From prototypes to the finished result, we meet the unique application requirements of our clients through personalized consultation, and superior manufacturing performance. The management team at ... 6.2: Potential, Kinetic, Free, and Activation Energy Energy associated with objects in motion is called kinetic energy. A speeding bullet, a walking person, the rapid movement of molecules in the air (which produces heat), and electromagnetic radiation like light all have kinetic energy. Now what if that same motionless wrecking ball is lifted two stories above a car with a crane?
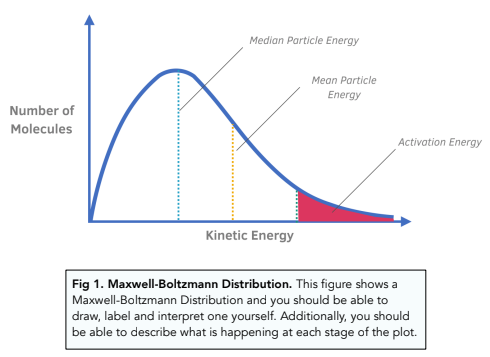
Kinetic Energy Distribution Chemistry Tutorial - AUS-e-TUTE The kinetic energy (Maxwell-Boltzmann) distribution curve for N 2 (g) molecules at 273 K and 1273 K is plotted and the activation energy (1250 × 10 -3 J) is shown in the graph below. Remember that the area under each curve represents the number of molecules within a given range of kinetic energies.
Heating and Cooling Curves - Kentchemistry.com Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy and a Heating Curve. Since Temperature is a measure of "Average Kinetic Energy", any change in temperature is a change in Kinetic Energy. ... On the heating curve diagram provided above, label each of the following regions: Liquid, only ; Gas, only; Phase change.
PDF Potential and Kinetic Energy S - Stanford University Potential and Kinetic Energy: Roller Coasters Student Version Key Concepts: • Energy is the ability of a system or object to perform work. It exists in various forms. • Potential energy is the energy an object has inside a force field due to its position. In the
› resource › hew06Energy in a Roller Coaster Ride | PBS LearningMedia This interactive roller coaster ride produced by WGBH illustrates the relationship between potential and kinetic energy. As the coaster cars go up and down the hills and around the loop of the track, a pie chart shows how the relative transformation back and forth between gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy.
Kinetic Energy - Definition, Units, Equation, Examples, Types, Videos ... The kinetic energy equation is given as: K E = 1 2 m v 2 Where KE is the kinetic energy, m is the body's mass, and v is the body's velocity. Deriving Kinetic Energy Equation Kinetic energy equation can be obtained by the basic process of computing the work (W) that is done by a force (F).
PDF STEMonstrations - Kinetic and Potential Energy - NASA Kinetic energy (KE) is a form of energy related to an object's motion. KE could be translation (moving from one place to ... Draw your roller coaster below and label the height of each hill in centimeters. Also label the area on each hill where potential energy is decreasing and kinetic energy is increasing.
2.10: Work and Kinetic Energy for a Many-Body System Total Mechanical Energy. The total mechanical energy \( E \) of a particle is defined as the sum of the kinetic and potential energies. \[\label{eq: 2.60} E = T + U \] Note that the potential energy is defined only to within an additive constant since the force \( \mathbf{F} = - \nabla U \) depends only on difference in potential energy.
Kinetic Energy Calculator In classical mechanics, kinetic energy (KE) is equal to half of an object's mass (1/2*m) multiplied by the velocity squared. For example, if a an object with a mass of 10 kg (m = 10 kg) is moving at a velocity of 5 meters per second (v = 5 m/s), the kinetic energy is equal to 125 Joules, or (1/2 * 10 kg) * 5 m/s 2 .
Kinetic Theory of Gases - NASA The model, called the kinetic theory of gases, assumes that the molecules are very small relative to the distance between molecules. The molecules are in constant, random motion and frequently collide with each other and with the walls of any container. The individual molecules possess the standard physical properties of mass, momentum, and energy.
Calculate Kinetic and Potential Energy - YouTube Dec 17, 2016 ... Key moments. View all · Kinetic energy Any object that moves will have kinetic energy The amount of kinetic energy an object has can be found ...
Potential And Kinetic Energy Labels Teaching Resources | TpT Students will have to show and label the greatest points of potential and kinetic energy, and tell where the energy came from. Included: -Suggestions for use -Mater Subjects: Other (Science), Science Grades: 5th - 7th Types: Activities, Laboratory, Worksheets Add to cart Wish List Roller Coaster Physics- Kinetic & Potential Energy by
1.3: Introduction to Kinetic and Potential Energy The equation for kinetic energy is KE = 1 2mv2 where KE is kinetic energy, m is mass, and v is velocity. This definition should make sense: big things moving fast have the most energy, the most ability to shove other things or knock them over, etc. Example 1.3.1: Kinetic Energy of an Object
Kinetic and Potential energy of Pendulum [Explained] Kinetic energy of a pendulum: For the pendulum of mass of bob 'm', moving with a tangential velocity of 'v', the kinetic energy is given by, `KE=\frac{1}{2}m.v^{2}` But as the mass of the bob is a constant quantity thus the kinetic energy of the pendulum totally depends on a velocity of a bob.
Potential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy Labeling Activity Potential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy Labeling Activity. Potential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy Labeling Activity. High Resolution Version of Activity for ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy Diagram for PowerPoint - PSlides The measurement of the kinetic energy is dependent on the mass and velocity of the object in question. From the calculation results in the exact measurement of the energy that is present. ... one going up, one on the crest and one heading down. It labels each one by kinetic energy in, potential energy and kinetic energy out. Download Now ...
Kinetic energy | Definition, Formula, Units, Examples, & Facts kinetic energy, form of energy that an object or a particle has by reason of its motion. If work, which transfers energy, is done on an object by applying a net force, the object speeds up and thereby gains kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is a property of a moving object or particle and depends not only on its motion but also on its mass.
Learn About Classical Kinetic Energy | Chegg.com The classical kinetic energy of an object depends on the mass of a body and its corresponding speed. The kinetic energy is equal to the product of the half ...
a. Draw a basic kinetic energy diagram. Include a | Chegg.com Draw a basic kinetic energy diagram. Include a line to represent activation energy for a reaction, and label the line.
Potential and Kinetic Energy | Texas Gateway Draw a diagram along with your explanation and label it to demonstrate where energy changes from kinetic to potential and back to kinetic. Good luck! Print ...
› science › biologyTypes of energy (article) | Khan Academy The energy associated with an object’s motion is called kinetic energy. A speeding bullet, a walking person, and electromagnetic radiation like light all have kinetic energy. Another example of kinetic energy is the energy associated with the constant, random bouncing of atoms or molecules.
Paper Roller Coasters: Kinetic and Potential Energy Roller coasters are an excellent way to teach your students about conservation of energy. Gravitational * potential energy is the amount of energy an object has due to its mass and its height off the ground. Kinetic energy is the amount of energy an object has due to its mass and its speed. When a roller coaster car reaches the top of its very ...
phys.libretexts.org › Bookshelves › College_Physics7.2: Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem Feb 20, 2022 · Kinetic energy is a form of energy associated with the motion of a particle, single body, or system of objects moving together. We are aware that it takes energy to get an object, like a car or the package in Figure, up to speed, but it may be a bit surprising that kinetic energy is proportional to speed squared.
Kinetic energy - Wikipedia The kinetic energy is equal to 1/2 the product of the mass and the square of the speed. In formula form: where is the mass and is the speed (magnitude of the velocity) of the body. In SI units, mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules .



















Komentar
Posting Komentar