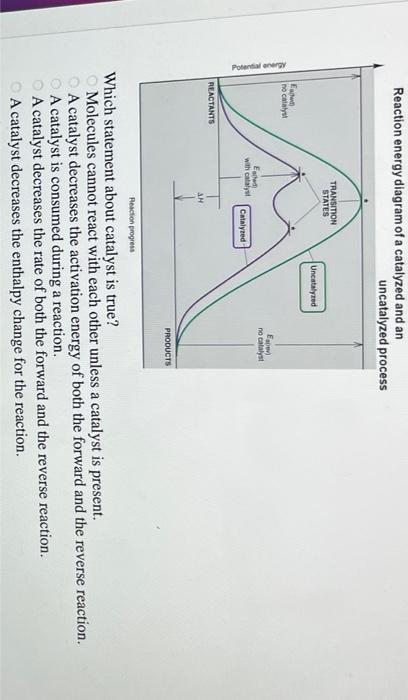
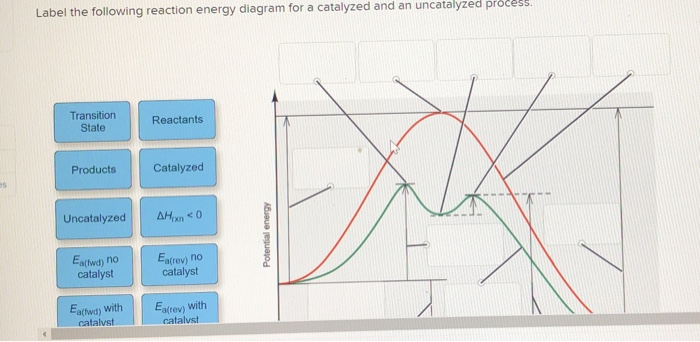
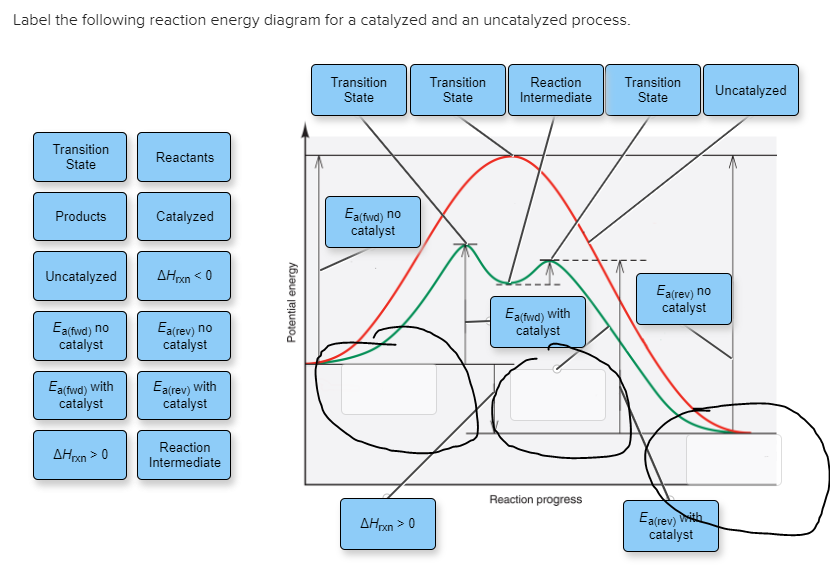
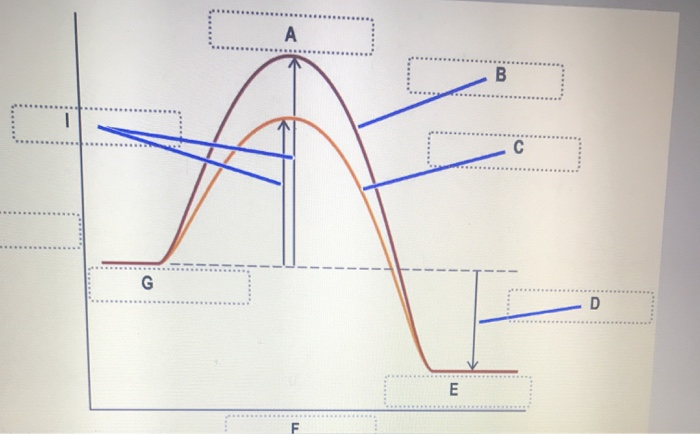
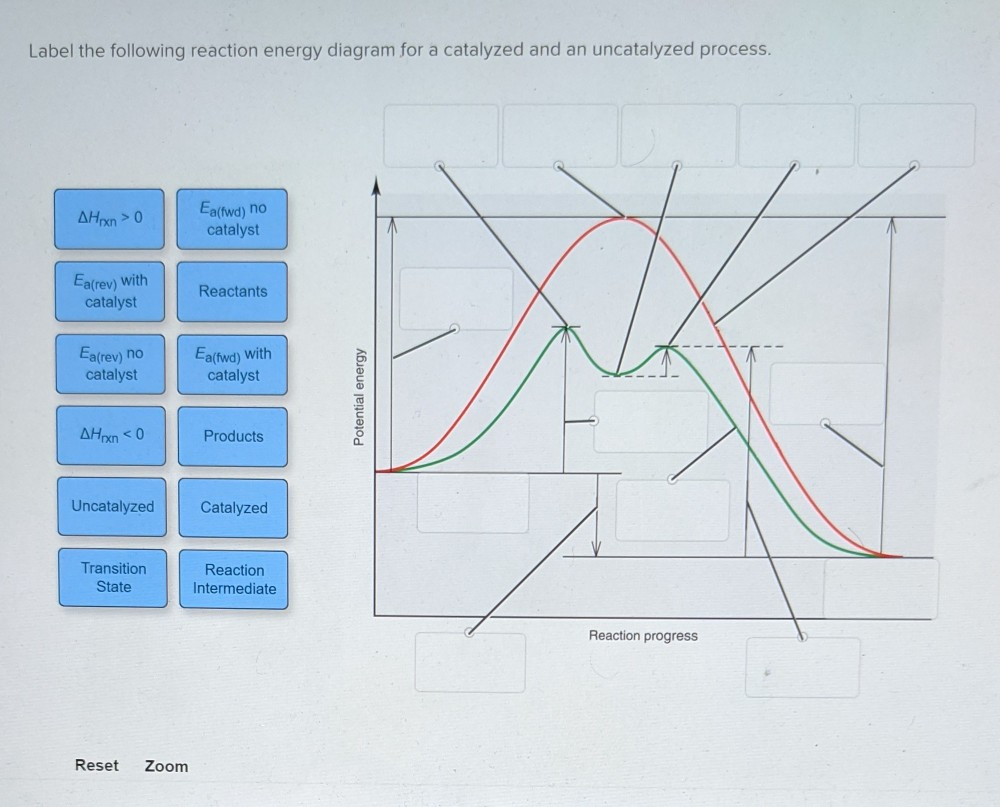
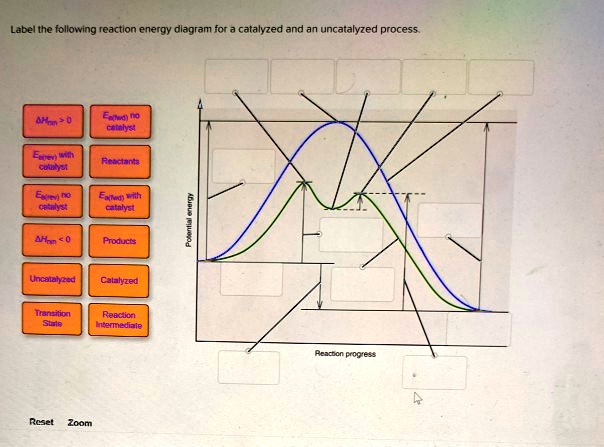
41 reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
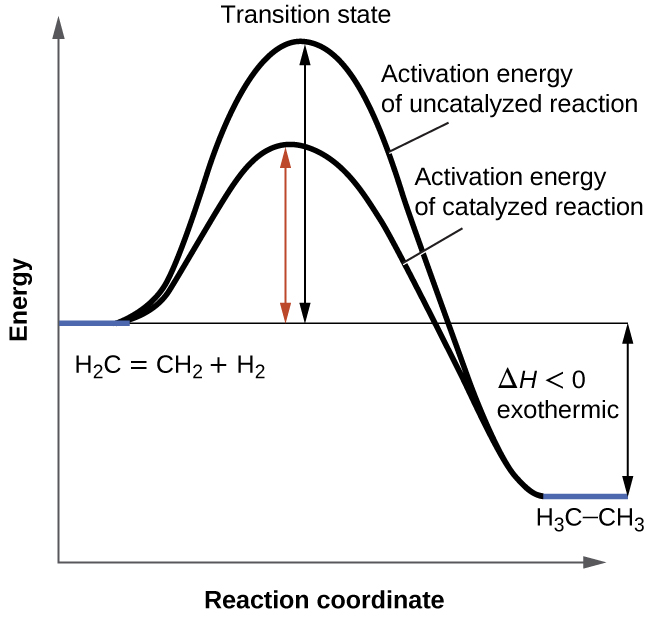
12.7: Catalysis - Chemistry LibreTexts One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 12.7. 1. Solved Label the following reaction energy diagram for a - Chegg Transition State Transition State Transition intermediate Reaction Intermediate Transition State Transition Uncatalyzed Transition State Reactants Products Catalyzed Ea (fwd) no catalyst Uncatalyzed AHxn < 0 Potential energy Ea (rev) no catalyst Ea (fwd) no catalyst Ea (rev) This problem has been solved!
12.7 Catalysis | Chemistry - Lumen Learning One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1.

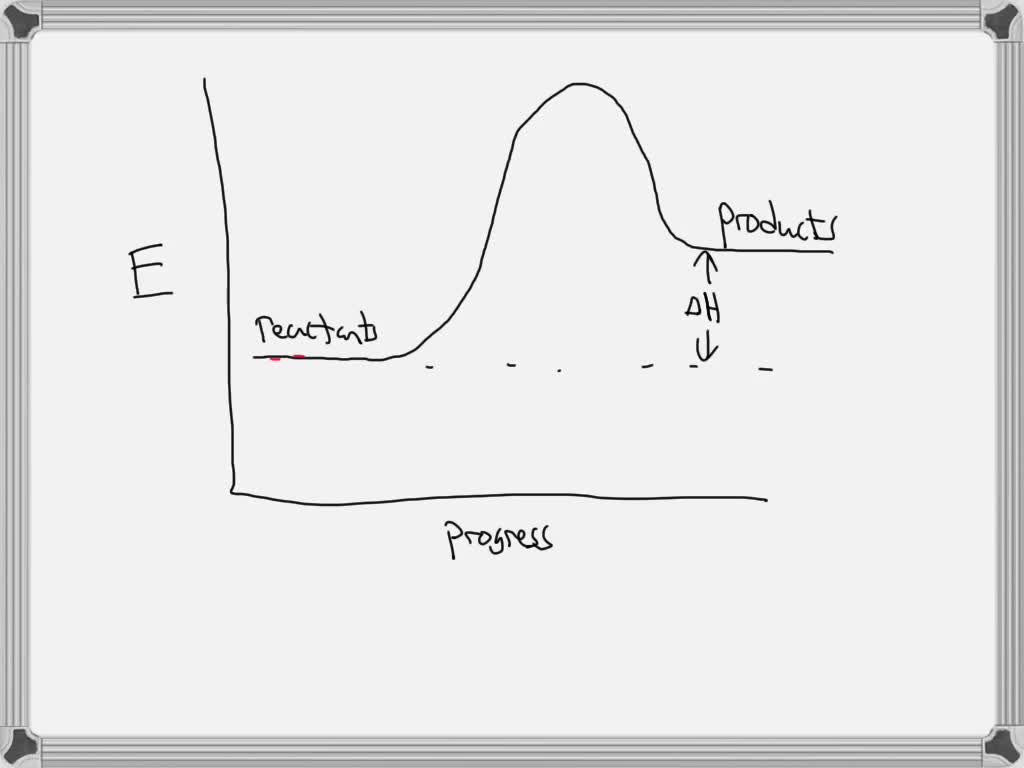
Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
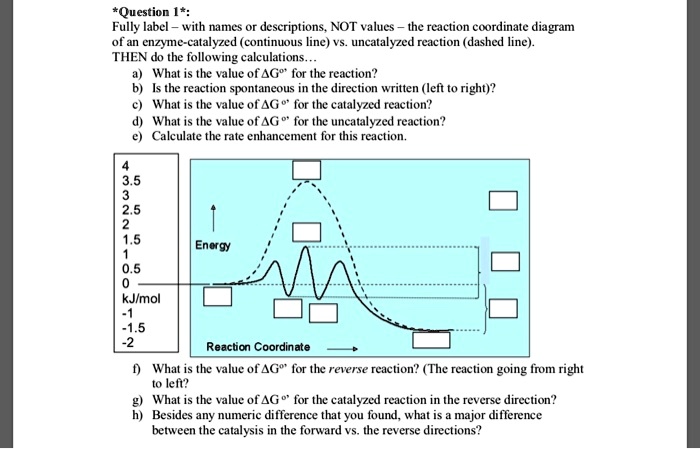
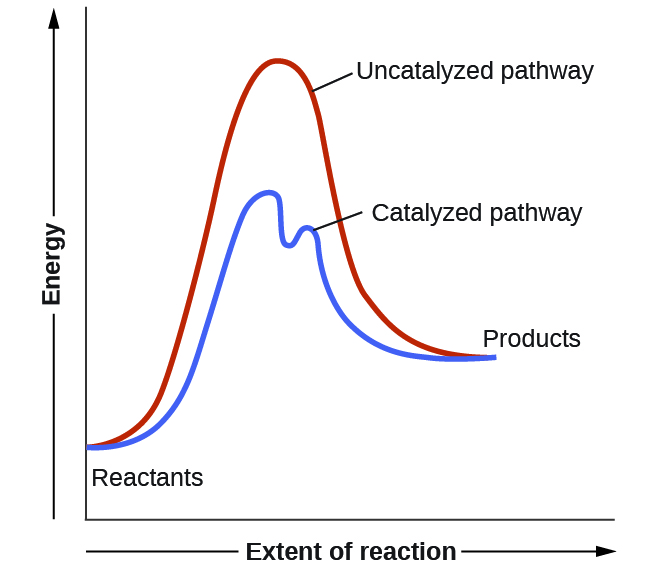
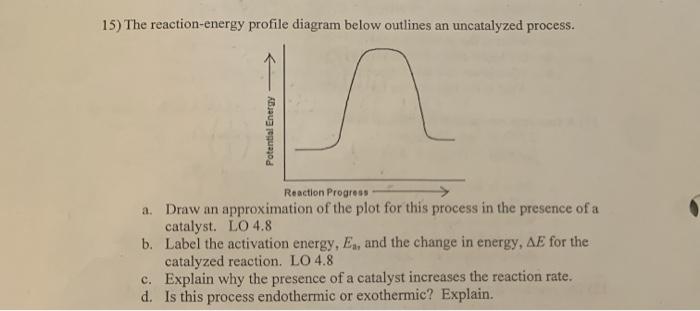
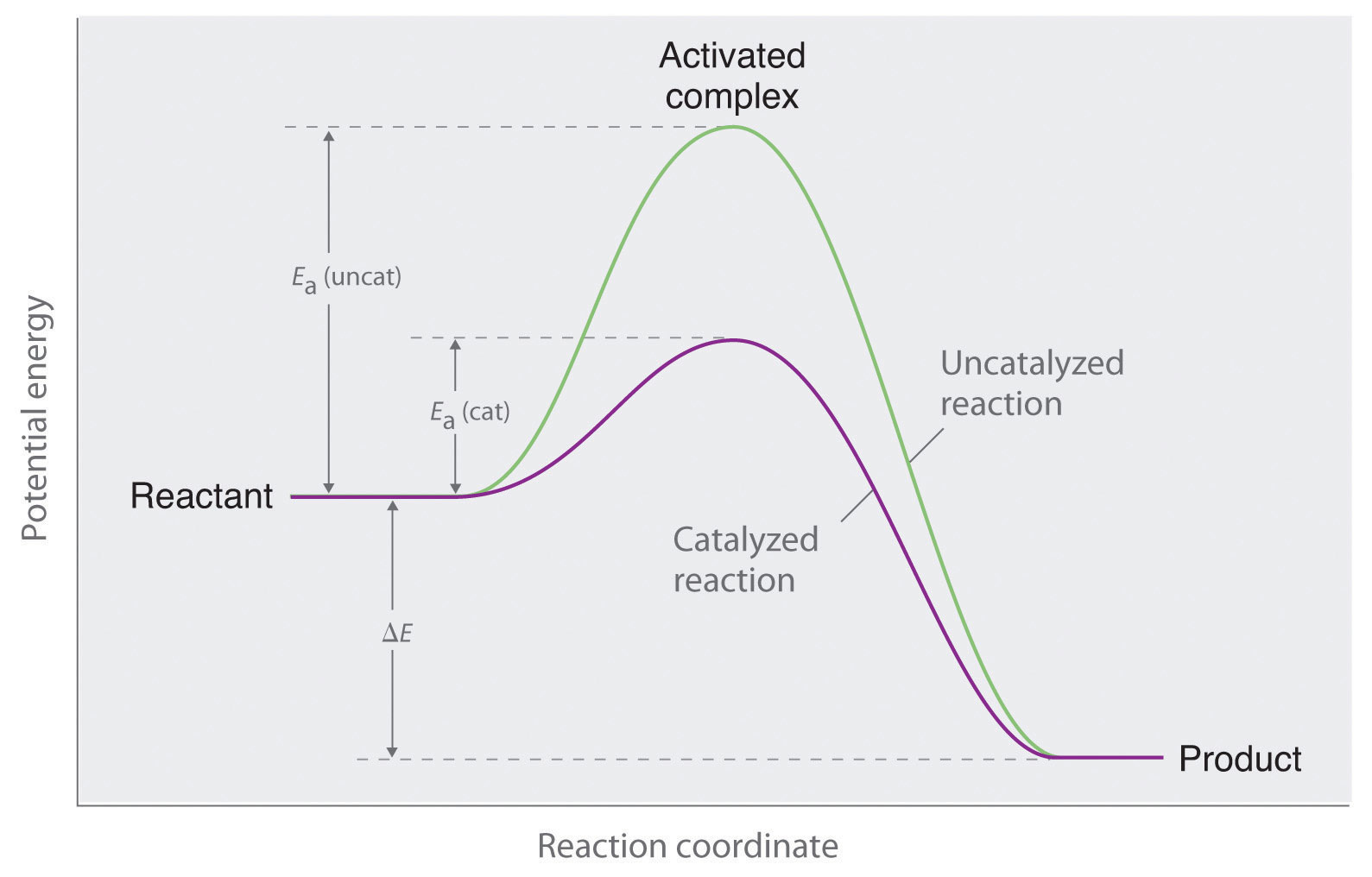
PDF AP CHEMISTRY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES - Unauthorized In process 2, covalent bonds (or sigma bonds, or electron-pair ... Consider the four reaction-energy profile diagrams shown below. (i) Identify the two diagrams that could represent a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed reaction pathway for the same reaction. Indicate which of the two diagrams represents the catalyzed reaction pathway for 14.7: Catalysis - Chemistry LibreTexts This graph compares potential energy diagrams for a single-step reaction in the presence and absence of a catalyst. The only effect of the catalyst is to lower the activation energy of the reaction. The catalyst does not affect the energy of the reactants or products (and thus does not affect ΔE). (CC BY-NC-SA; anonymous) Potential Energy Diagram of Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed Reactions Potential Energy Diagram of Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed Reactions Narcademy 1.94K subscribers Subscribe 58 Share 3.7K views 2 years ago #narcademy Analyzing the potential energy diagram of...
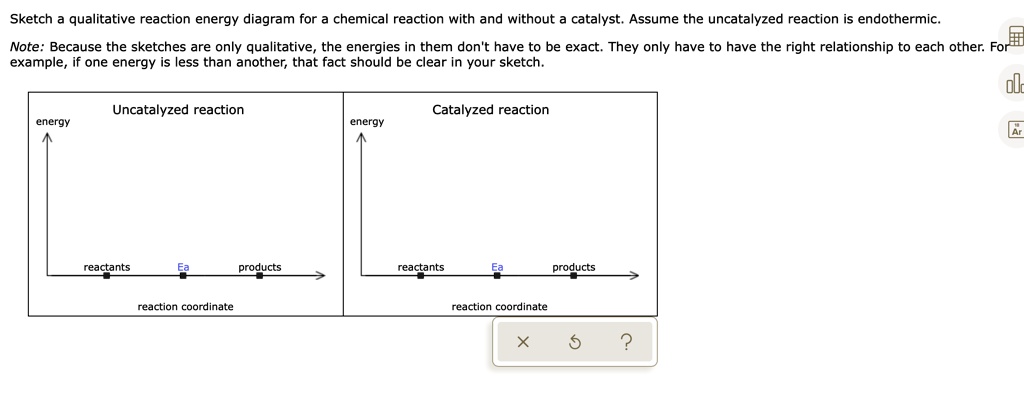
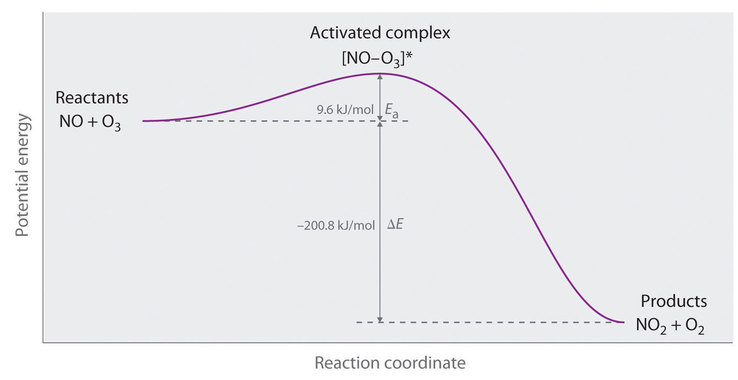
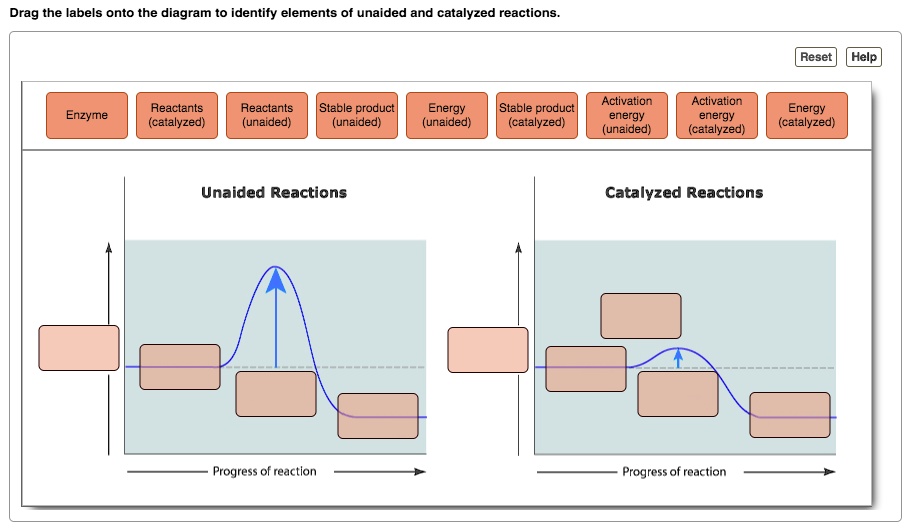
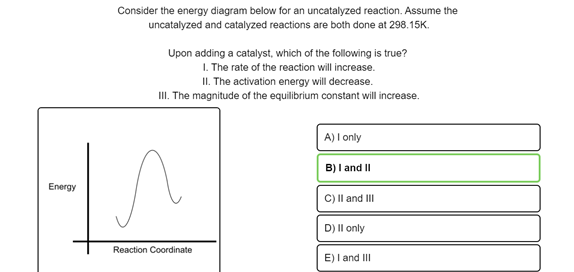
Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Solved Label the following reaction energy diagram for a | Chegg.com Question: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process Transition State Reactants Products Catalyzed Uncatalyzed AHxn <0 Potential energy Eartwa, no catalyst Entrev) no catalyst Ea (wa) with Ea (rev) with catalyst catalyst B. Transition Stato Reactants Products Catalyzed Uncatalyzed AH 0 Potentialergy … Catalysis | Chemistry for Majors - Lumen Learning Example 1: Using Reaction Diagrams to Compare Catalyzed Reactions. The two reaction diagrams here represent the same reaction: one without a catalyst and one with a catalyst. Estimate the activation energy for each process, and identify which one involves a catalyst. Activation energy (article) | Khan Academy The activation energy shown in the diagram below is for the forward reaction (reactants \rightarrow → products), which is exergonic. If the reaction were to proceed in the reverse direction (endergonic), the transition state would remain the same, but the activation energy would be larger. 12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax For the first step, Ea = 80 kJ for (a) and 70 kJ for (b), so diagram (b) depicts the catalyzed reaction. Activation energies for the second steps of both mechanisms are the same, 20 kJ. Homogeneous Catalysts A homogeneous catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants.
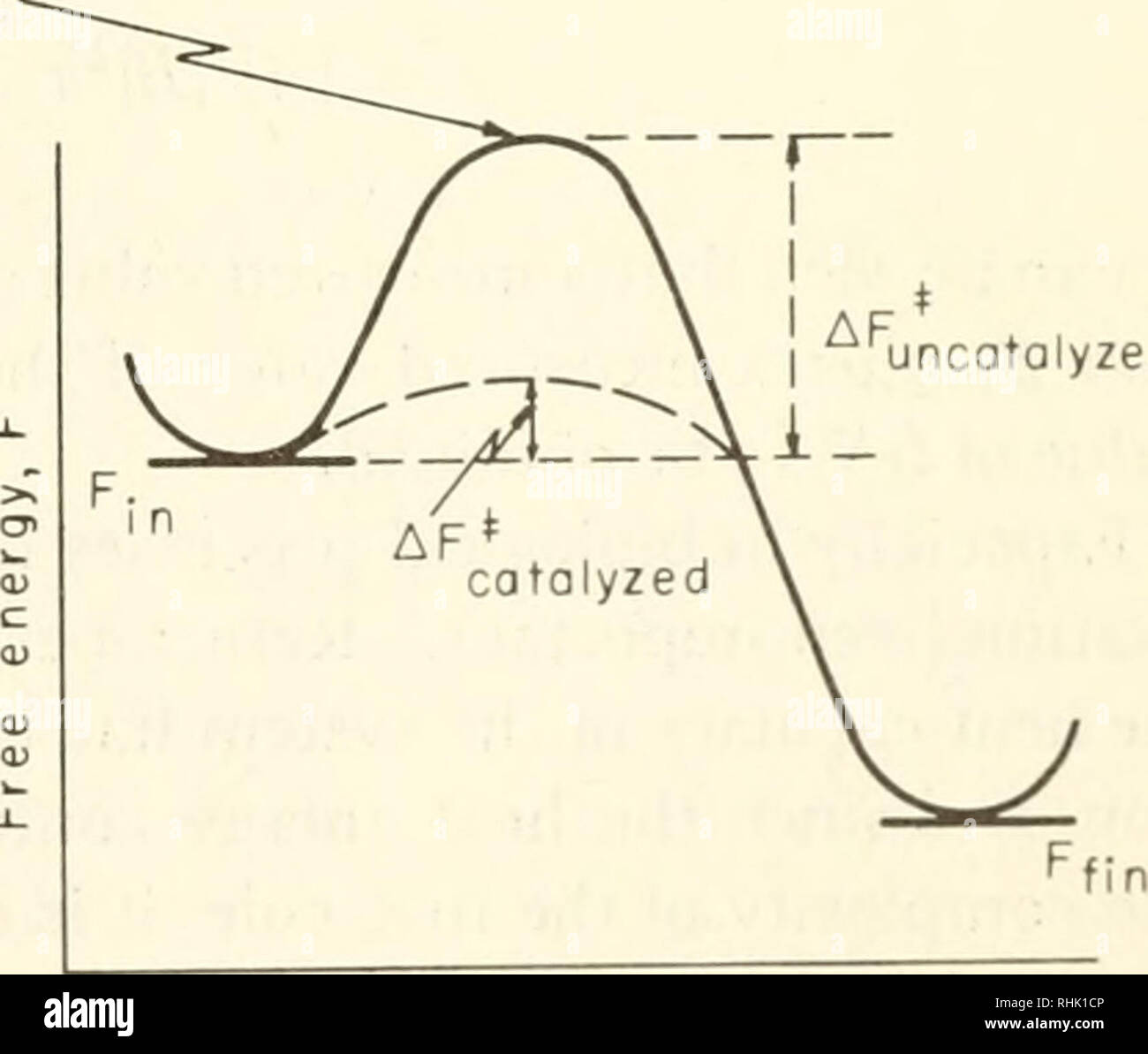
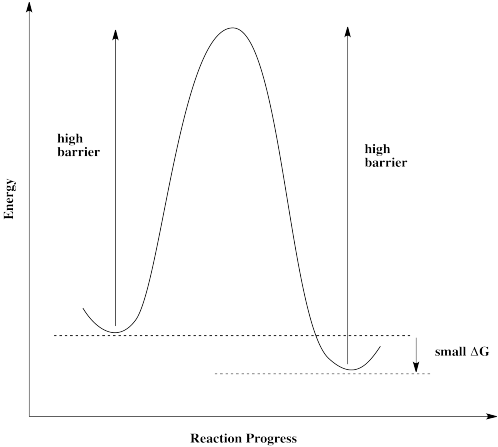
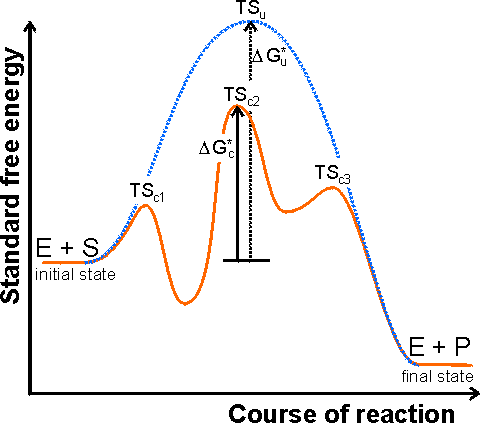
Catalysts Definition and How They Work - ThoughtCo A catalyst is a chemical substance that affects the rate of a chemical reaction by altering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed. This process is called catalysis. A catalyst is not consumed by the reaction and it may participate in multiple reactions at a time. The only difference between a catalyzed reaction and an uncatalyzed reaction is that the activation energy is ... Types of catalysts (article) | Kinetics | Khan Academy Notice that the energies of the reactants and products are the same for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reaction. Therefore, the overall energy released during the reaction, Δ H rxn \Delta \text H_{\text{rxn}} Δ H rxn delta, start text, H, end text, start subscript, start text, r, x, n, end text, end subscript, does not change when you add the enzyme. . This emphasizes a very important point ... Energy diagrams for enzyme‐catalyzed reactions: Concepts and ... The energy diagram for a reaction model consisting of one enzyme, one substrate, and one product is depicted in many books where it is compared with that for the uncatalyzed reaction. The survey of several Biochemistry textbooks reveals a high diversity of profiles for the same process. Potential Energy Diagram of Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed Reactions Potential Energy Diagram of Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed Reactions Narcademy 1.94K subscribers Subscribe 58 Share 3.7K views 2 years ago #narcademy Analyzing the potential energy diagram of...
14.7: Catalysis - Chemistry LibreTexts This graph compares potential energy diagrams for a single-step reaction in the presence and absence of a catalyst. The only effect of the catalyst is to lower the activation energy of the reaction. The catalyst does not affect the energy of the reactants or products (and thus does not affect ΔE). (CC BY-NC-SA; anonymous) PDF AP CHEMISTRY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES - Unauthorized In process 2, covalent bonds (or sigma bonds, or electron-pair ... Consider the four reaction-energy profile diagrams shown below. (i) Identify the two diagrams that could represent a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed reaction pathway for the same reaction. Indicate which of the two diagrams represents the catalyzed reaction pathway for














Komentar
Posting Komentar